No man can serve two masters: for either he will hate the one, and love the other; or else he will hold to the one, and despise the other. Ye cannot serve God and mammon.
(Matthew 6:24 KJV)
This teaching popped into my mind a few weeks ago and while reflecting on where our morality has broken down in the United States. Mammon is an interesting Biblical word and refers to more than just money as currency. Jesus is not talking about having material wealth here, rather he’s addressing about misplaced trust and devotion put in it. And “serve” seems like a key operational word here. In Greek it is “douleuó” (δουλεύω) and the term refers to slavery or bondage.
Jesus was confronted on this teaching by the Pharisees—who we’re told sneered at him. But we are also told they were the same people who would shortchange their own parents by abusing the practice of ‘Corban’—by claiming money was set aside for God (Matt. 15:1-9, Mark 7:1-13)—when it was all about their own gain. When you’re addicted to material gain, you’d likely sell off your own mother for another hit of the money drug and can’t be a good person. A slave to the ‘almighty dollar’ will basically do any evil to obtain more of it.
For we brought nothing into the world, and we can take nothing out of it. But if we have food and clothing, we will be content with that. Those who want to get rich fall into temptation and a trap and into many foolish and harmful desires that plunge people into ruin and destruction. For the love of money is a root of all kinds of evil. Some people, eager for money, have wandered from the faith and pierced themselves with many griefs.
(1 Timothy 6:7-10 NIV)
Pray for contentment, not cash. You can have enough to eat and live without a big bank account. We may enjoy—or imagine—a feeling of security from having more, but it is false security and pursuit of it leads to moral compromise. As Mark 8:36 asks: “What good is it for someone to gain the whole world, yet forfeit their soul?”
The American Evangelical landscape does not handle this very well. The ‘health and wealth” or prosperity gospel might not be openly preached in every church, but there’s often the underlying assumption that those who have money are blessed. I mean, you don’t want to ever offend those who fill the offering plate, do you?
This errant belief that material success equates to divine favor has seeped deeply into political alliances, particularly among Evangelicals who have thrown their support behind leaders promising them economic prosperity above all else. Donald Trump, with his gilded persona and “art of the deal” ethos, became a symbol of this worldview—tremendously blessed by wealth, endorsed by faith leaders, and appearing to be toualluntouchable.


Yet, as his second term unfolds, we’re now seeing how devotion to money over all else manifests in government—prioritizing billionaire gains over accountability and human suffering. It isn’t the paradise promised.
Life Under Bondi-age
One of the big reasons Trump had seemed like a better choice than a continuation of a Biden administration, under Harris, was his ‘green’ policies. He appeared to be a “make money, not war” candidate, given his history of draft dodging and no new war first term. Maybe it was just weariness of the conflicts in Gaza and Ukraine that made him a hope to the “it’s the economy, stupid” crowd. He also promised to release the Epstein files—which would mean some justice, right?

Attorney General Pam Bondi’s testimony to Congress is a revelation of a mentality that is completely detached. Who knows who coached her—or maybe it was completely her own idea? But the answers she gave only raised more eyebrows.
For example, when asked:
How many of Epstein’s co-conspirators have you indicted? How many perpetrators are you even investigating?
She replied:
Because Donald Trump, the Dow, the Dow right now is over — the Dow is over $50,000. I don’t know why you’re laughing. You’re a great stock trader, as I hear, Raskin. The Dow is over 50000 right now, the S&P at almost 7,000, and the Nasdaq smashing records. Americans’ 401(k)s and retirement savings are booming. That’s what we should be talking about. We should be talking about making Americans safe. We should be talking about — what does the Dow have to do with anything? That’s what they just asked. Are you kidding?
Is she kidding?
That’s astonishingly callous.
With victims in the crowd, she really thought it would play well to deflect with a pivot to a stock market highs?
Now, sure, this sort of hearing is a very partisan and high-pressure event. And a great many of those lawmakers are guilty of a cover-up as the Trump administration. Lest we forget it, around 80% to 90% of Epstein’s political donations went to Democrats. But now responsibility for the continued lack of transparency about this lies squarely on the Trump administration.
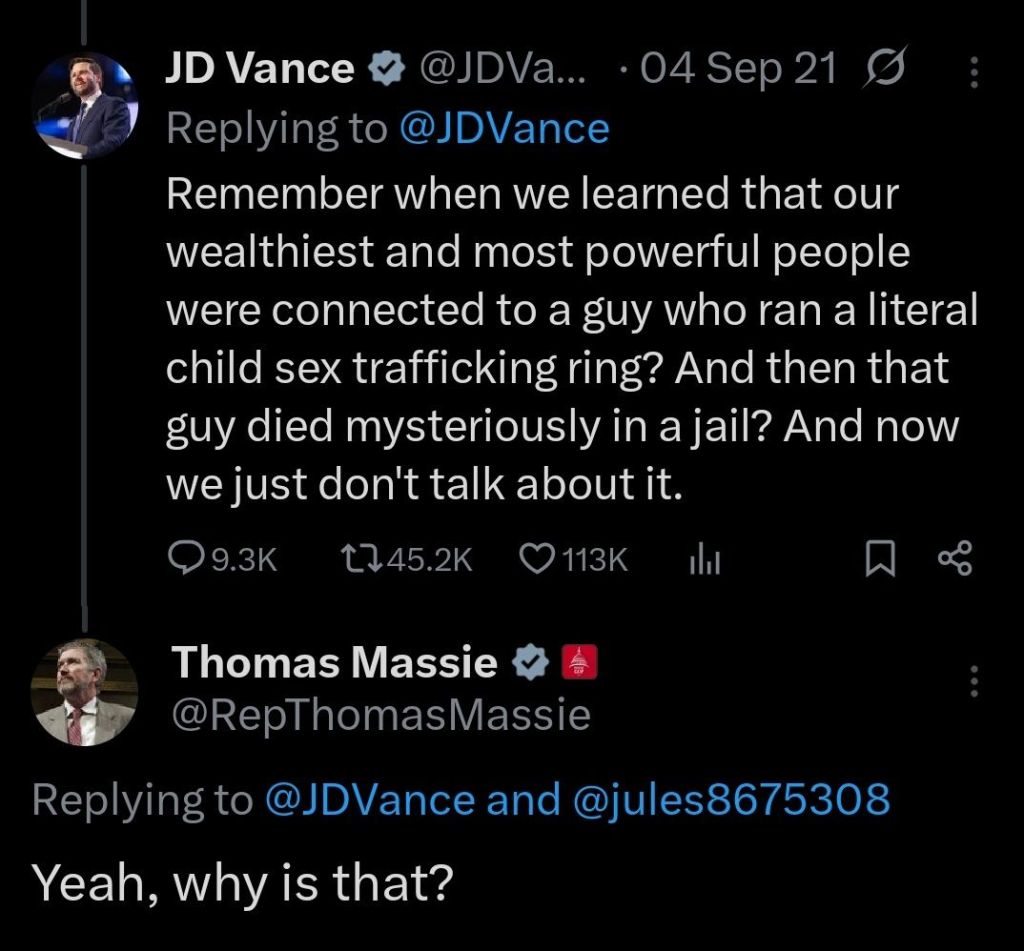
Bondi’s Justice Department has violated the law, The Epstein Files Transparency Act—a bill demanding the unredacted release of the files pushed through by representatives Thomas Massie (R) and Ro Khanna (D), by continued use of redactions that extends a cover-up that has gone on for decades. And both parties are neck-deep in this scandal, which is why nothing was done about it last administration despite Trump’s name being in the files tens of thousands of times—and probably many more mentions still hidden under all those black lines.
The administration that ran on a promise to tell the truth about Epstein has become one where Trump gaslights:
Are you still talking about Jeffrey Epstein? This guy’s been talked about for years, are people still talking about this guy? This creep? That is unbelievable. I can’t believe you’re asking a question on Epstein at a time like this, when we’re having some of the greatest success, and also tragedy with what happened in Texas. It just seems like a desecration.
I mean, why would we still be talking about a guy who was apparently sex trafficking a bunch of underage girls to a very long list of elites who have yet to be prosecuted, right?
The truth is a ‘desecration’ of Texas flooding response somehow?

Wherever the case, Bondi isn’t a fraction as skilled as her boss at this game. If you are going to pivot off a question about horrible sexual crimes and ritual abuse not leading to dozens of arrests, then at least deflect away to matters of an equal moral weight. As in this “We have arrested X amount of pedophiles, more than any administration since Genghis Khan—we’re making America safe again!” That would sound much less tone deaf than turning to the economy as if this nullifies questions about Epstein.
What does Bondi’s pivot scream?
It shouts that money can take her attention off of crime—that she can be bribed. More importantly, it suggests she thinks we will be distracted by money and forget about a total lack of prosecutions.

In the end, Bondi’s deflection and the Trump administration’s broader pattern reveals the stark truth: when mammon reigns supreme, justice for the vulnerable becomes optional, and the soul of a nation is quietly sold off in exchange for an economy that mostly benefits billionaires. True contentment—and true greatness or lasting gain—will never come from chasing a dollar or at expense of seeking justice for all people.
The crazy part is that most who voted for Trump thinking it would help their portfolio and would keep us out of war—will find out that those who bought him have no problem with sending your sons to die in Iran.