The battery electric vehicle (EV) versus the internal combustion engine (ICE) powered debate is one of the most irrational of our time. On both sides of the discussion, you have those frothing-at-the-mouth types who attack the moment you disagree. And this is exactly the response that I got after I had casually mentioned that ICE is 1/3 the cost under a click-bait post…

One just called me ignorant, but others tried to make an argument, including this response:
I’m trying to figure out what car cost 1/3 of the price of a Tesla🤔🤔? The long range Model 3 (the one you want for a roadtrip) is $42,500 – $7500 tax credit is $35,000. This is not factoring in gas savings. Please tell me what new car is availability for under $12,000 (that’s the 1/3 cost of a Tesla you mentioned)?
Fair enough question.
Note, I never said new, but assuming that I did…
Believe it or not, and even in this inflationary age, there are still reliable sedans that come in under $20,000. Starting with a Mitsubishi Mirage G4 ($18,500), the Kia Rio ($17,875), and the Nissan Versa ($17,075), the lowest-priced option is half of even the subsidized price of the Tesla base model.
But you can’t exclude the subsidy from the cost of the EV, the government doesn’t have a magic wand to create value and we all end up paying for their expenditures in our taxes or by inflation due to money printing. And it only begins with that “tax credit” (so-called) given directly to privileged people who can afford a new luxury car.
What is the true cost of subsidies?
According to a study by the Texas Public Policy Foundation, the cost to us is nearly $50,000 for every EV produced:
Federal and state subsidies and regulatory credits for EVs totaled nearly $22 billion in 2021, or nearly $50,000 per EV, socializing the true cost of these vehicles to taxpayers, utility ratepayers, and owners of gasoline vehicles
Tens of billions of dollars have been spent trying to make EVs viable, and yet still the average cost of these vehicles is $65,000, compared to $48,000 for ICE. Why haven’t these subsidies leveled the playing field? It is simply the fact that batteries require tons of extra material and a much more complex process to produce.
So we can at least double that visible “tax credit” subsidy and already the true cost of an EV is close to three times a comparable ICE sedan.
We could stop there—the 1/3 number reached—but let’s continue…
What is the true cost of production?
The cost of a vehicle isn’t just the window sticker price or the money that it takes to manufacture. The bigger question—given the reason many say we should switch to EVs is about emissions—is what the increased environmental impact is of producing the batteries that go into these cars. Is this a trade-off we are willing to make?

Lithium batteries are costly, they require an enormous amount of water and also leave a toxic legacy that will grow exponentially as EV is adopted. Is it worth this cost to only marginally reduce carbon emissions? That is to say, around 17-30% less emissions according to European Energy Agency?
Sure, it could get better with a heavy investment in electrical generation and transmission—yet that is another huge cost financially and environmentally…
What is the cost of infrastructure demand?
This is where the conversation is the most interesting. We have the refining capacity and distribution network already built for ICE vehicles. Gasoline and diesel fuel have the advantage of being energy-dense and can be moved around using the existing highways. But what about EVs?
There is an illusion that comes with plugging something in. The load we put on the system is invisible. But there is no magic to it. Electricity is something that must be produced somewhere and then transmitted to the charging stations. If everyone adopted EV technology the grid would collapse.
We’re currently nowhere even near what it would take in capacity to convert everyone to EV. The easiest route to more electrical generation is to go anuclear. So how many new nuclear power plants would it take? Well, if we use miles driven and the number of cars on the road today, then we would need to build 250 additional nuclear power plants as big as the largest plant in the US, and the supporting infrastructure to keep up with this demand.

So are you willing to have a Palo Verde in your own backyard?
It cost 5.9 billion dollars to build one in 1988 (the equivalent of 13.9 billion in 2023) and we needed to start building 250 of them yesterday. The solar and wind equivalent would be even more costly to build and maintain.
The costs would be astronomical and that’s just considering only passenger vehicles. Switching Class 8 trucks would take even more of these massive power plants and spending—the cost of switching would be insane. Not to mention you would need more trucks to do the same work as you did with diesel. And remember, every dime that we spend on this mass EV conversion could go to health care or education instead.
Can you now see how extremely costly EVs will become as they are adopted?
But it does not end there…
Why is the cost of wear items greater?
Batteries are heavy and weight is the enemy of “wear items” like brakes or tires—which is not to mention the additional damage to the highway infrastructure.

EV tires wear 20% faster than comparable ICE vehicles. That is a cost out of your own pocket and also a concern for the environment. And do not forget, to be safe you’ll need those heavy-duty EV-specific tires. Sure, maybe this is not a very big problem for those who can already afford the premium cost of a new EV? However, for that waitress struggling to make ends meet she will have to make the choice between safety and home utilities.
Next up is excess road wear. Big trucks are obviously the leading cause of damage to roads. However, EV proliferation will start to cause problems for existing infrastructure:
A 6,000-pound vehicle causes more than five times as much road damage as a 4,000-pound sedan. A GMC Hummer EV, which weighs 9,063 pounds, will cause 116 times as much road damage as a Honda Civic, weighing 2,762 pounds.
The article cited above isn’t about EVs yet does apply given it is about the vehicle weight. Even the Model 3 is a whopping 3,862 to 4,054 lbs. Sure, one vehicle is not going to do a whole lot by itself, but the volume over time will significantly impact bridges and parking garages that were designed for lighter ICE vehicles. This EV vehicle weight bloat caused by batteries will require very costly upgrades to prevent catastrophic failures—like the Ann Street Building Collapse:


Speaking of disasters. With EV there is potential for a thermal runaway or reaction that can’t be stopped—like an ICE fire—by simply denying the source of oxygen. This hazard will result in more damage to road surfaces, more time spent in traffic jams after incidents, and additional toxic emissions. This is a cost to be seriously considered with all of the others.
Cost of time, capability, and resale value…
Many of the costs and drawbacks of EVs are hidden under a pile of subsidies or are moved upstream like the emissions—out of sight out of mind.
But what cannot be ignored is performance in terms of range. Time is by far our most valuable resource and nobody wants to spend hours in a place they don’t want to be because their vehicle battery is drained.
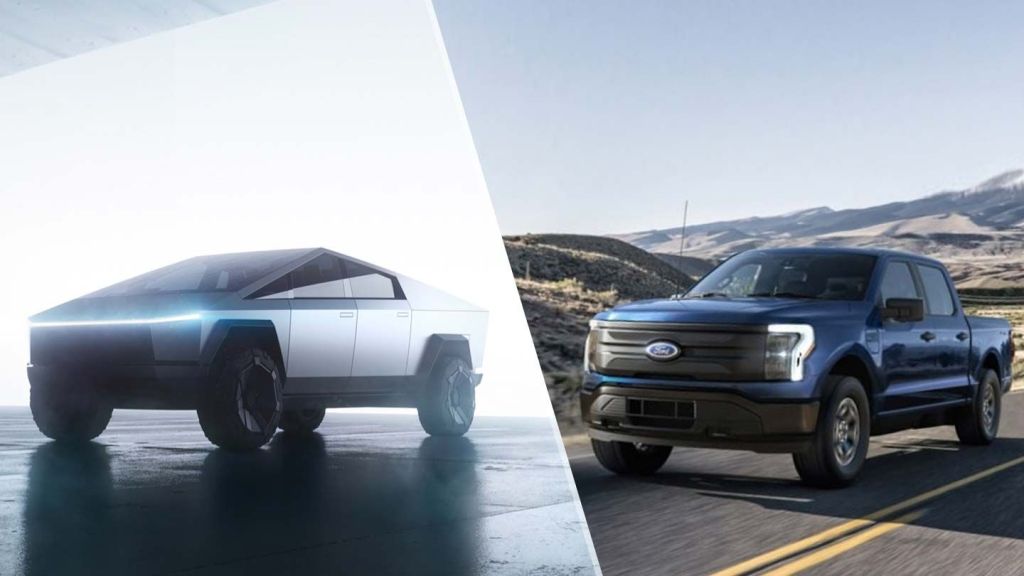
As far as capabilities, even EV trucks are useless for towing, both the Tesla Cybertruck and the Ford Lightning—both costing around $100,000 in the higher trim levels—aren’t so good at doing typical truck things. Sure, they produce a ton of low-end torque and are very fast. But the F-150 EV only went 90 miles pulling a camper and the Tesla only fared a little better.

And finally, we need to talk about plunging resale values. For a while EV was a novelty, the “way of the future” every suburban geek needed to virtue signal. But it appears that this is now starting to fade and reality is starting to take over again—46% of EV owners in the US plan to ditch EV to return back to ICE—and many will not recoup their cost because the floor is dropping out for used EVs:
A recent study from iSeeCars.com showed the average price of a 1- to 5-year-old used EV in the U.S. fell 31.8% over the past 12 months, equating to a value loss of $14,418. In comparison, the average price for a comparably aged internal combustion engine vehicle fell just 3.6%.
That’s bad news for the EV industry. That is probably why Ford, after losing billions on their EV investments, has made plans to pivot back to hybrid. Toyota, ever conservative, never made the mistake of getting sucked into the EV mania. My wife’s C-Max (hybrid) has no range anxiety, saves fuel, and has a plug-in version that can go on battery for a length of a commute. This is the right compromise.
ICE costs less to build, but the hybrid will likely emerge as the winner for being the best of both worlds. It has range like ICE, and torque like an EV, while also keeping its value and not requiring vast new expenditures to upgrade the electrical infrastructure. If costs are reflected in the market hybrid will come out victorious in the end. Some can afford EVs today, but only because others are absorbing more than half of the real costs.
As a footnote, I’m not opposed to EVs nor do I think they are destined to go extinct. If resale values continue to drop I would even consider owning one. The whole point of this article is simply to give a bit of pushback against the Pollyannaish sentiments that would lead to an ill-advised mandate. There would be an enormous cost, and opportunity cost, that would come with this. Just the fact that EVs need massive subsidies to be sold should tell us enough. If it isn’t viable in the market it isn’t viable.